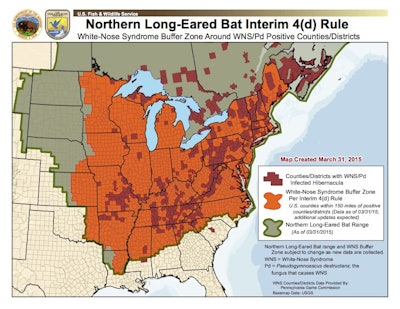
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service on Wednesday listed the northern long eared bat as a threatened species and also released interim rule 4(d) to lessen impact on the forest industry.
The interim rule (4(d) will allow forest management practices and limited tree removal projects to continue unabated in areas impacted by WNS or within the WNS buffer zone as long as they:
- occur more than a quarter mile away from a known, occupied bat hibernacula
- avoid cutting or destroying known, occupied roost trees from June 1–July 31
- avoid clearcuts or similar harvest methods within a quarter mile of known, occupied roost trees.
The species is currently known to live in 37 states, and WNS has been discovered in 28 of those states, according to the USFWS.
The vast range of the bat and the protections afforded to it by the threatened listing has forest industry organizations concerned. Among them, The Hardwood Federation has been lobbying legislators on the industry’s behalf.
There will be a 90-day open comment period on the rule before it is finalized.
The listing becomes effective May 4.
 The interim 4(d) rule impacts forest operations in northern long eared bat habitat.
The interim 4(d) rule impacts forest operations in northern long eared bat habitat.
























